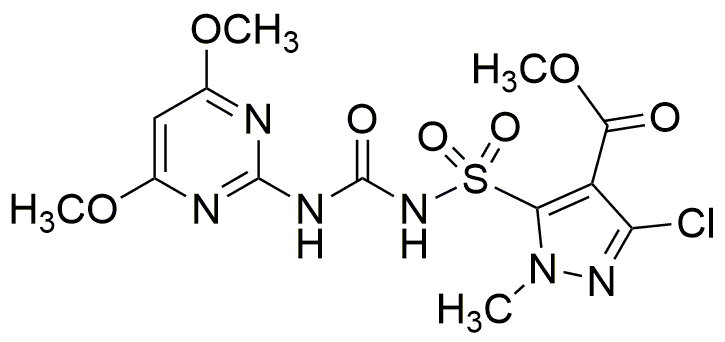
Halosulfuron-methyl is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Agricultural Weed Control: This herbicide is primarily used in agriculture to manage a variety of broadleaf weeds in crops such as rice and turf. Its selective action helps protect desired plants while effectively controlling unwanted vegetation.
- Environmental Studies: Researchers use Halosulfuron-methyl to study its environmental impact, including its degradation in soil and water. Understanding its behavior helps in assessing the safety and sustainability of agricultural practices.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): This chemical plays a role in IPM strategies, where it is combined with other pest control methods to reduce reliance on chemical inputs, promoting more sustainable farming practices.
- Crop Yield Improvement: By effectively controlling weeds, Halosulfuron-methyl contributes to higher crop yields. Farmers can achieve better productivity and profitability while minimizing competition for nutrients and water.
- Research on Herbicide Resistance: Scientists study Halosulfuron-methyl to understand mechanisms of herbicide resistance in weed populations, which is crucial for developing effective management strategies and ensuring long-term agricultural viability.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Halosulfuron-methyl is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Agricultural Weed Control: This herbicide is primarily used in agriculture to manage a variety of broadleaf weeds in crops such as rice and turf. Its selective action helps protect desired plants while effectively controlling unwanted vegetation.
- Environmental Studies: Researchers use Halosulfuron-methyl to study its environmental impact, including its degradation in soil and water. Understanding its behavior helps in assessing the safety and sustainability of agricultural practices.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): This chemical plays a role in IPM strategies, where it is combined with other pest control methods to reduce reliance on chemical inputs, promoting more sustainable farming practices.
- Crop Yield Improvement: By effectively controlling weeds, Halosulfuron-methyl contributes to higher crop yields. Farmers can achieve better productivity and profitability while minimizing competition for nutrients and water.
- Research on Herbicide Resistance: Scientists study Halosulfuron-methyl to understand mechanisms of herbicide resistance in weed populations, which is crucial for developing effective management strategies and ensuring long-term agricultural viability.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.