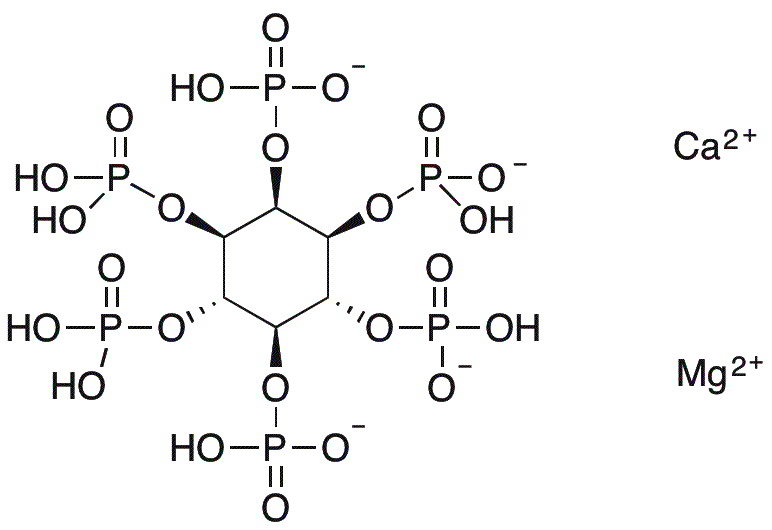
Phytin is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Nutritional Supplements: Phytin is used as a source of phosphorus in dietary supplements, promoting bone health and overall nutrition.
- Food Preservation: Its antioxidant properties help in extending the shelf life of various food products by preventing oxidative damage.
- Animal Feed: Phytin is incorporated into animal feed formulations to enhance the nutritional value, particularly in poultry and swine, improving growth rates and health.
- Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, phytin is explored for its potential in drug delivery systems, aiding in the controlled release of active compounds.
- Biotechnology: Researchers utilize phytin in biotechnological applications, such as in the development of biosensors and bioassays due to its unique chemical properties.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Phytin is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Nutritional Supplements: Phytin is used as a source of phosphorus in dietary supplements, promoting bone health and overall nutrition.
- Food Preservation: Its antioxidant properties help in extending the shelf life of various food products by preventing oxidative damage.
- Animal Feed: Phytin is incorporated into animal feed formulations to enhance the nutritional value, particularly in poultry and swine, improving growth rates and health.
- Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, phytin is explored for its potential in drug delivery systems, aiding in the controlled release of active compounds.
- Biotechnology: Researchers utilize phytin in biotechnological applications, such as in the development of biosensors and bioassays due to its unique chemical properties.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.