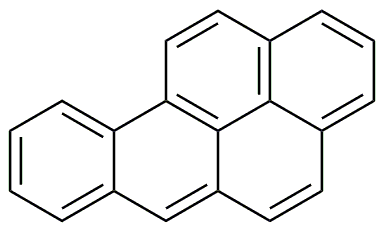
3,4-Benzopyrene is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Environmental Monitoring: This compound is a key marker for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil and water testing, helping researchers assess pollution levels and environmental health.
- Cancer Research: Due to its carcinogenic properties, it is extensively studied in cancer biology to understand mechanisms of tumor formation and the effects of environmental toxins on human health.
- Material Science: It serves as a model compound for studying the thermal and chemical stability of materials, particularly in the development of flame-retardant materials.
- Analytical Chemistry: Used as a standard in chromatographic techniques, it aids in the calibration of instruments for detecting and quantifying PAHs in various samples.
- Toxicology Studies: It is employed in toxicological assessments to evaluate the effects of exposure to carcinogens, providing insights into safety regulations and public health guidelines.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
3,4-Benzopyrene is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Environmental Monitoring: This compound is a key marker for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil and water testing, helping researchers assess pollution levels and environmental health.
- Cancer Research: Due to its carcinogenic properties, it is extensively studied in cancer biology to understand mechanisms of tumor formation and the effects of environmental toxins on human health.
- Material Science: It serves as a model compound for studying the thermal and chemical stability of materials, particularly in the development of flame-retardant materials.
- Analytical Chemistry: Used as a standard in chromatographic techniques, it aids in the calibration of instruments for detecting and quantifying PAHs in various samples.
- Toxicology Studies: It is employed in toxicological assessments to evaluate the effects of exposure to carcinogens, providing insights into safety regulations and public health guidelines.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.