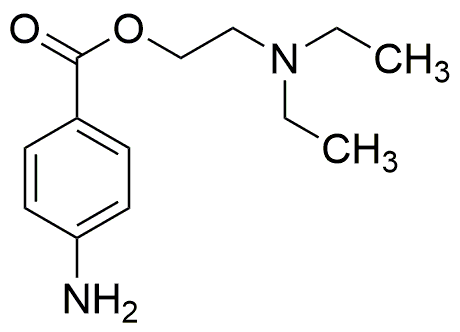
Procaine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Local Anesthesia: Commonly used in dental procedures and minor surgeries, it provides effective pain relief by blocking nerve signals in a specific area.
- Pharmaceutical Formulations: Often incorporated into injectable medications, it enhances the delivery of active ingredients, improving patient comfort during administration.
- Veterinary Medicine: Utilized in animal care, it serves as a local anesthetic for various procedures, ensuring the well-being of pets and livestock during treatment.
- Research Applications: Employed in laboratory settings to study nerve function and pain pathways, aiding in the development of new analgesics and anesthetics.
- Combination Therapies: Used in conjunction with other medications to enhance therapeutic effects, it can improve outcomes in pain management protocols.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Procaine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Local Anesthesia: Commonly used in dental procedures and minor surgeries, it provides effective pain relief by blocking nerve signals in a specific area.
- Pharmaceutical Formulations: Often incorporated into injectable medications, it enhances the delivery of active ingredients, improving patient comfort during administration.
- Veterinary Medicine: Utilized in animal care, it serves as a local anesthetic for various procedures, ensuring the well-being of pets and livestock during treatment.
- Research Applications: Employed in laboratory settings to study nerve function and pain pathways, aiding in the development of new analgesics and anesthetics.
- Combination Therapies: Used in conjunction with other medications to enhance therapeutic effects, it can improve outcomes in pain management protocols.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.