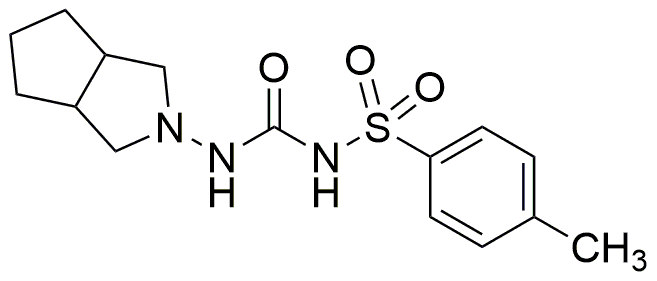
Gliclazide is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Diabetes Management: Primarily used as an oral hypoglycemic agent, it helps control blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes, making it essential for endocrinology practices.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Researchers explore its mechanisms and efficacy, contributing to the development of new diabetes medications and improving existing treatment protocols.
- Clinical Trials: Frequently involved in clinical studies to assess its effectiveness and safety, providing valuable data for healthcare professionals and regulatory bodies.
- Combination Therapies: Often used in conjunction with other antidiabetic agents, enhancing overall glucose control and offering a more comprehensive treatment approach for patients.
- Patient Education: Used in educational programs for diabetes management, helping patients understand the importance of medication adherence and lifestyle changes for better health outcomes.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Gliclazide is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Diabetes Management: Primarily used as an oral hypoglycemic agent, it helps control blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes, making it essential for endocrinology practices.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Researchers explore its mechanisms and efficacy, contributing to the development of new diabetes medications and improving existing treatment protocols.
- Clinical Trials: Frequently involved in clinical studies to assess its effectiveness and safety, providing valuable data for healthcare professionals and regulatory bodies.
- Combination Therapies: Often used in conjunction with other antidiabetic agents, enhancing overall glucose control and offering a more comprehensive treatment approach for patients.
- Patient Education: Used in educational programs for diabetes management, helping patients understand the importance of medication adherence and lifestyle changes for better health outcomes.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.