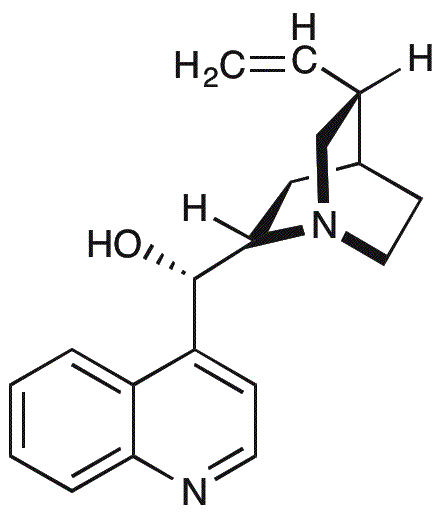
Cinchonine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Pharmaceutical Development: Cinchonine is a key compound in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical agents, particularly in the development of antimalarial drugs. Its ability to inhibit the growth of malaria parasites makes it invaluable in tropical medicine.
- Analytical Chemistry: This compound serves as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric synthesis, helping chemists create enantiomerically pure compounds. Its effectiveness in improving yields and selectivity is crucial for the production of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Natural Product Research: Cinchonine is often studied for its potential health benefits, including its role in traditional medicine. Researchers explore its effects on various biological pathways, which may lead to new therapeutic applications.
- Food and Beverage Industry: The compound is used as a flavoring agent in certain beverages, providing a unique taste profile. Its natural origin appeals to consumers seeking authentic and traditional flavors.
- Biochemical Research: Cinchonine is utilized in studies investigating its interaction with various biological molecules, contributing to our understanding of enzyme mechanisms and receptor binding, which is essential for drug design.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Cinchonine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Pharmaceutical Development: Cinchonine is a key compound in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical agents, particularly in the development of antimalarial drugs. Its ability to inhibit the growth of malaria parasites makes it invaluable in tropical medicine.
- Analytical Chemistry: This compound serves as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric synthesis, helping chemists create enantiomerically pure compounds. Its effectiveness in improving yields and selectivity is crucial for the production of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Natural Product Research: Cinchonine is often studied for its potential health benefits, including its role in traditional medicine. Researchers explore its effects on various biological pathways, which may lead to new therapeutic applications.
- Food and Beverage Industry: The compound is used as a flavoring agent in certain beverages, providing a unique taste profile. Its natural origin appeals to consumers seeking authentic and traditional flavors.
- Biochemical Research: Cinchonine is utilized in studies investigating its interaction with various biological molecules, contributing to our understanding of enzyme mechanisms and receptor binding, which is essential for drug design.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.