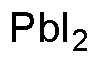Lead(II) iodide is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Photovoltaic Cells: This compound is a key material in perovskite solar cells, which are known for their high efficiency and low production costs. Researchers are exploring its use to improve energy conversion rates.
- Optoelectronic Devices: Lead(II) iodide is used in the fabrication of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photodetectors, enhancing performance in devices that require efficient light absorption and emission.
- Medical Imaging: In certain imaging techniques, lead(II) iodide serves as a contrast agent, improving the visibility of structures in X-ray imaging, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Environmental Monitoring: The compound is utilized in sensors for detecting heavy metals in water, providing critical data for environmental protection and public health initiatives.
- Research in Material Science: Its unique properties make it a subject of study for developing new materials with tailored electronic and optical characteristics, which can lead to advancements in various technologies.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Lead(II) iodide is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Photovoltaic Cells: This compound is a key material in perovskite solar cells, which are known for their high efficiency and low production costs. Researchers are exploring its use to improve energy conversion rates.
- Optoelectronic Devices: Lead(II) iodide is used in the fabrication of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photodetectors, enhancing performance in devices that require efficient light absorption and emission.
- Medical Imaging: In certain imaging techniques, lead(II) iodide serves as a contrast agent, improving the visibility of structures in X-ray imaging, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Environmental Monitoring: The compound is utilized in sensors for detecting heavy metals in water, providing critical data for environmental protection and public health initiatives.
- Research in Material Science: Its unique properties make it a subject of study for developing new materials with tailored electronic and optical characteristics, which can lead to advancements in various technologies.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.