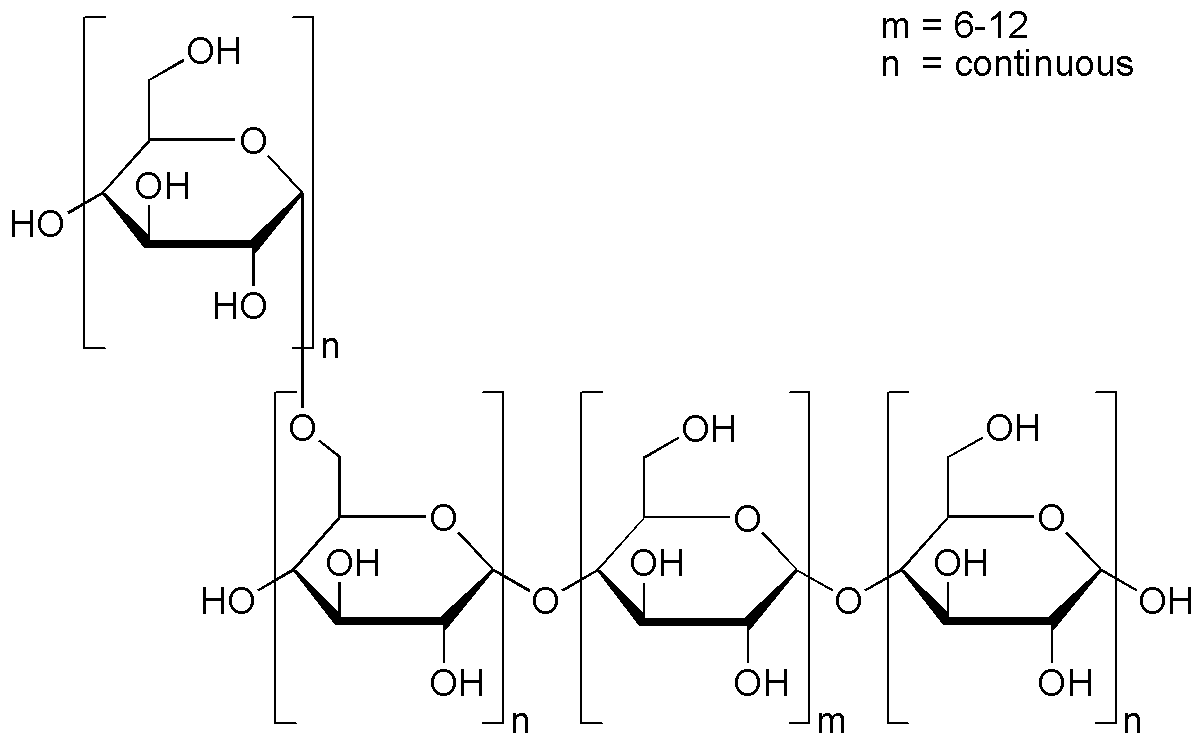
D-(+)-Glycogen is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Biotechnology: It serves as a crucial energy source in cell culture systems, enhancing cell growth and productivity in biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used as a stabilizer in drug formulations, it helps maintain the efficacy and shelf-life of medications, particularly in injectables.
- Nutrition: Commonly found in dietary supplements, it supports energy metabolism and recovery in athletes, making it a popular choice for sports nutrition products.
- Cosmetics: Incorporated in skincare formulations, it acts as a humectant, providing moisture retention and improving skin texture.
- Research Applications: Utilized in studies involving glycogen metabolism, it aids in understanding various metabolic disorders and developing potential treatments.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
D-(+)-Glycogen is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Biotechnology: It serves as a crucial energy source in cell culture systems, enhancing cell growth and productivity in biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used as a stabilizer in drug formulations, it helps maintain the efficacy and shelf-life of medications, particularly in injectables.
- Nutrition: Commonly found in dietary supplements, it supports energy metabolism and recovery in athletes, making it a popular choice for sports nutrition products.
- Cosmetics: Incorporated in skincare formulations, it acts as a humectant, providing moisture retention and improving skin texture.
- Research Applications: Utilized in studies involving glycogen metabolism, it aids in understanding various metabolic disorders and developing potential treatments.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.