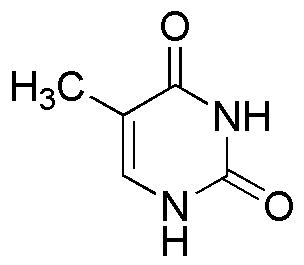
Thymine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- DNA Synthesis: Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in DNA, essential for genetic material synthesis. Researchers use it to study genetic sequences and develop synthetic DNA for various applications.
- Biotechnology: In genetic engineering, thymine plays a crucial role in creating recombinant DNA. This is vital for producing genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that can enhance agricultural productivity.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Thymine derivatives are explored in drug formulation, particularly in antiviral and anticancer therapies, offering potential benefits over traditional compounds due to their targeted action.
- Diagnostic Tools: Thymine is used in the development of molecular probes for detecting specific DNA sequences, aiding in diagnostics for genetic disorders and infectious diseases.
- Research on Nucleic Acid Stability: Studies on thymine's interactions help scientists understand nucleic acid stability and mutations, which is crucial for advancing fields like genetics and molecular biology.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Thymine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- DNA Synthesis: Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in DNA, essential for genetic material synthesis. Researchers use it to study genetic sequences and develop synthetic DNA for various applications.
- Biotechnology: In genetic engineering, thymine plays a crucial role in creating recombinant DNA. This is vital for producing genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that can enhance agricultural productivity.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Thymine derivatives are explored in drug formulation, particularly in antiviral and anticancer therapies, offering potential benefits over traditional compounds due to their targeted action.
- Diagnostic Tools: Thymine is used in the development of molecular probes for detecting specific DNA sequences, aiding in diagnostics for genetic disorders and infectious diseases.
- Research on Nucleic Acid Stability: Studies on thymine's interactions help scientists understand nucleic acid stability and mutations, which is crucial for advancing fields like genetics and molecular biology.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.