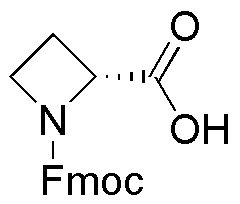
Fmoc-D-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Peptide Synthesis: This compound serves as a key building block in the synthesis of peptides, particularly in solid-phase peptide synthesis, allowing for the creation of complex, biologically active molecules.
- Drug Development: It plays a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry for developing new drugs, especially those targeting specific receptors, enhancing the efficacy and selectivity of therapeutic agents.
- Bioconjugation: Researchers use it to facilitate bioconjugation processes, linking biomolecules with drugs or imaging agents, which is crucial in targeted therapy and diagnostics.
- Material Science: The compound is applied in the development of novel materials, including polymers and nanomaterials, which can be used in various applications such as drug delivery systems.
- Research in Chemical Biology: It is utilized in studies that explore protein interactions and functions, providing insights into cellular processes and potential therapeutic targets.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Fmoc-D-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Peptide Synthesis: This compound serves as a key building block in the synthesis of peptides, particularly in solid-phase peptide synthesis, allowing for the creation of complex, biologically active molecules.
- Drug Development: It plays a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry for developing new drugs, especially those targeting specific receptors, enhancing the efficacy and selectivity of therapeutic agents.
- Bioconjugation: Researchers use it to facilitate bioconjugation processes, linking biomolecules with drugs or imaging agents, which is crucial in targeted therapy and diagnostics.
- Material Science: The compound is applied in the development of novel materials, including polymers and nanomaterials, which can be used in various applications such as drug delivery systems.
- Research in Chemical Biology: It is utilized in studies that explore protein interactions and functions, providing insights into cellular processes and potential therapeutic targets.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.