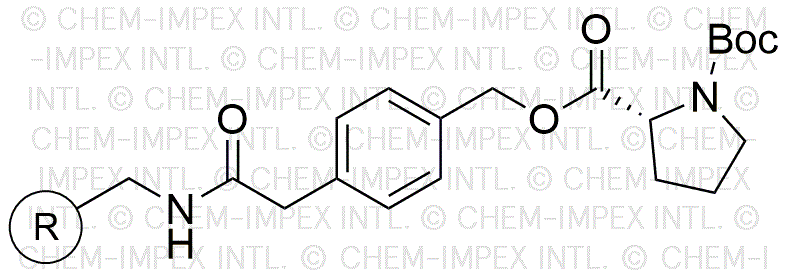
Boc-D-proline 4-oxymethylphenylacetamidomethyl is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Peptide Synthesis: This compound serves as a key building block in the synthesis of peptides, particularly in the development of peptide-based drugs and therapeutics.
- Drug Development: Its structural properties make it valuable in the design of novel pharmaceutical agents, especially in targeting specific biological pathways.
- Bioconjugation: The compound is used in bioconjugation techniques, allowing researchers to attach biomolecules to surfaces or other molecules, enhancing drug delivery systems.
- Research in Neuroscience: It plays a role in studying neurological pathways due to its ability to mimic natural amino acids, aiding in the understanding of brain function and disorders.
- Material Science: The compound is also explored in the development of new materials, particularly those that require specific functional groups for enhanced performance in various applications.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Boc-D-proline 4-oxymethylphenylacetamidomethyl is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Peptide Synthesis: This compound serves as a key building block in the synthesis of peptides, particularly in the development of peptide-based drugs and therapeutics.
- Drug Development: Its structural properties make it valuable in the design of novel pharmaceutical agents, especially in targeting specific biological pathways.
- Bioconjugation: The compound is used in bioconjugation techniques, allowing researchers to attach biomolecules to surfaces or other molecules, enhancing drug delivery systems.
- Research in Neuroscience: It plays a role in studying neurological pathways due to its ability to mimic natural amino acids, aiding in the understanding of brain function and disorders.
- Material Science: The compound is also explored in the development of new materials, particularly those that require specific functional groups for enhanced performance in various applications.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.