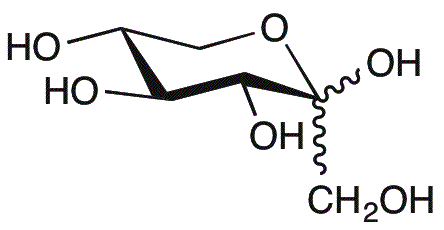
D-(+)-Sorbose is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Food Industry: It serves as a low-calorie sweetener and flavor enhancer, making it ideal for sugar-free and reduced-calorie products. Its unique sweetness profile can improve the taste of various food items without adding significant calories.
- Pharmaceuticals: D-(+)-Sorbose is used in the formulation of certain medications and supplements, particularly those aimed at managing blood sugar levels. Its properties can help in stabilizing active ingredients.
- Biotechnology: This compound is a key substrate in the production of vitamin C through fermentation processes. Its use in microbial fermentation can lead to more sustainable and cost-effective production methods.
- Cosmetics: In the cosmetic industry, it is incorporated into skincare products for its moisturizing properties. It can help improve skin hydration and texture, making it a valuable ingredient in creams and lotions.
- Research Applications: D-(+)-Sorbose is often used in biochemical research as a carbon source in microbial growth studies, allowing researchers to explore metabolic pathways and enzyme activities effectively.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
D-(+)-Sorbose is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Food Industry: It serves as a low-calorie sweetener and flavor enhancer, making it ideal for sugar-free and reduced-calorie products. Its unique sweetness profile can improve the taste of various food items without adding significant calories.
- Pharmaceuticals: D-(+)-Sorbose is used in the formulation of certain medications and supplements, particularly those aimed at managing blood sugar levels. Its properties can help in stabilizing active ingredients.
- Biotechnology: This compound is a key substrate in the production of vitamin C through fermentation processes. Its use in microbial fermentation can lead to more sustainable and cost-effective production methods.
- Cosmetics: In the cosmetic industry, it is incorporated into skincare products for its moisturizing properties. It can help improve skin hydration and texture, making it a valuable ingredient in creams and lotions.
- Research Applications: D-(+)-Sorbose is often used in biochemical research as a carbon source in microbial growth studies, allowing researchers to explore metabolic pathways and enzyme activities effectively.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.