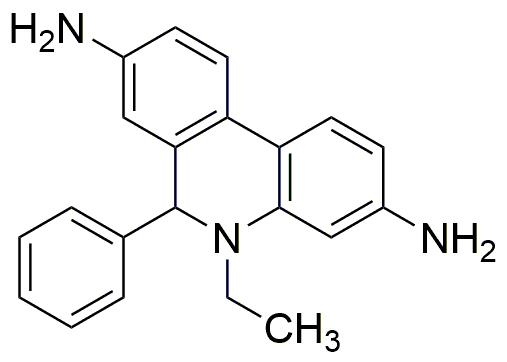
Dihydroethidium is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Cellular Imaging: This compound is frequently used as a fluorescent probe to visualize reactive oxygen species (ROS) in live cells, helping researchers study oxidative stress and its implications in various diseases.
- Neuroscience Research: Dihydroethidium is employed to investigate neurodegenerative conditions by tracking oxidative damage in neuronal cells, providing insights into potential therapeutic targets.
- Cardiovascular Studies: In cardiology, it aids in assessing oxidative stress in heart tissues, allowing for a better understanding of heart diseases and the development of antioxidant therapies.
- Drug Development: The compound is used in pharmacological studies to evaluate the efficacy of new drugs aimed at reducing oxidative stress, which is linked to numerous health issues.
- Environmental Monitoring: Dihydroethidium can be applied in studies assessing the impact of pollutants on cellular health, providing valuable data for environmental research and public health initiatives.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Dihydroethidium is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Cellular Imaging: This compound is frequently used as a fluorescent probe to visualize reactive oxygen species (ROS) in live cells, helping researchers study oxidative stress and its implications in various diseases.
- Neuroscience Research: Dihydroethidium is employed to investigate neurodegenerative conditions by tracking oxidative damage in neuronal cells, providing insights into potential therapeutic targets.
- Cardiovascular Studies: In cardiology, it aids in assessing oxidative stress in heart tissues, allowing for a better understanding of heart diseases and the development of antioxidant therapies.
- Drug Development: The compound is used in pharmacological studies to evaluate the efficacy of new drugs aimed at reducing oxidative stress, which is linked to numerous health issues.
- Environmental Monitoring: Dihydroethidium can be applied in studies assessing the impact of pollutants on cellular health, providing valuable data for environmental research and public health initiatives.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.