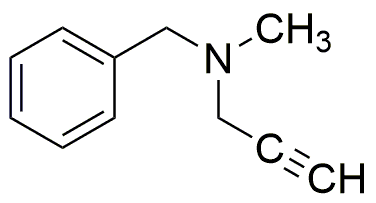
Pargyline is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Neuroprotection: Pargyline is used in studies investigating its potential to protect neurons from damage, particularly in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's. Its ability to inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) can help increase levels of neurotransmitters, which is beneficial in maintaining cognitive function.
- Antidepressant Research: Researchers explore its role as an antidepressant due to its MAO-inhibiting properties. This can lead to enhanced mood and emotional well-being, making it a subject of interest in the development of new antidepressant therapies.
- Cardiovascular Studies: Pargyline has applications in cardiovascular research, where it is examined for its effects on blood pressure regulation and vascular health, potentially offering benefits in managing hypertension.
- Pharmaceutical Development: The compound serves as a valuable reference in the synthesis of other pharmaceuticals, particularly those targeting neurological conditions, due to its unique chemical structure and properties.
- Research on Aging: Pargyline is investigated for its potential effects on aging processes, particularly in extending lifespan in model organisms, which could have implications for age-related health issues.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Pargyline is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Neuroprotection: Pargyline is used in studies investigating its potential to protect neurons from damage, particularly in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's. Its ability to inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) can help increase levels of neurotransmitters, which is beneficial in maintaining cognitive function.
- Antidepressant Research: Researchers explore its role as an antidepressant due to its MAO-inhibiting properties. This can lead to enhanced mood and emotional well-being, making it a subject of interest in the development of new antidepressant therapies.
- Cardiovascular Studies: Pargyline has applications in cardiovascular research, where it is examined for its effects on blood pressure regulation and vascular health, potentially offering benefits in managing hypertension.
- Pharmaceutical Development: The compound serves as a valuable reference in the synthesis of other pharmaceuticals, particularly those targeting neurological conditions, due to its unique chemical structure and properties.
- Research on Aging: Pargyline is investigated for its potential effects on aging processes, particularly in extending lifespan in model organisms, which could have implications for age-related health issues.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.