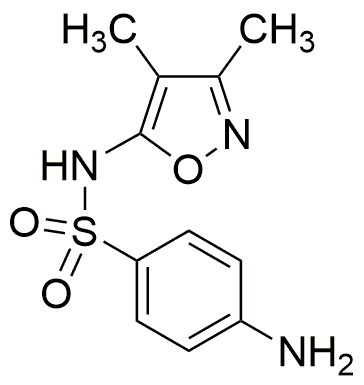
Sulfisoxazole is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Antibacterial Treatments: Commonly used in the formulation of antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, especially in pediatric medicine.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Serves as a key compound in drug formulation research, helping scientists develop new medications with enhanced efficacy.
- Analytical Chemistry: Employed in laboratory settings for the analysis of sulfonamide antibiotics, aiding in quality control and regulatory compliance.
- Veterinary Medicine: Used to treat infections in animals, providing effective solutions for veterinarians in managing bacterial diseases.
- Research on Drug Resistance: Plays a role in studies investigating bacterial resistance mechanisms, helping researchers develop strategies to combat resistant strains.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Sulfisoxazole is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Antibacterial Treatments: Commonly used in the formulation of antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, especially in pediatric medicine.
- Pharmaceutical Development: Serves as a key compound in drug formulation research, helping scientists develop new medications with enhanced efficacy.
- Analytical Chemistry: Employed in laboratory settings for the analysis of sulfonamide antibiotics, aiding in quality control and regulatory compliance.
- Veterinary Medicine: Used to treat infections in animals, providing effective solutions for veterinarians in managing bacterial diseases.
- Research on Drug Resistance: Plays a role in studies investigating bacterial resistance mechanisms, helping researchers develop strategies to combat resistant strains.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.