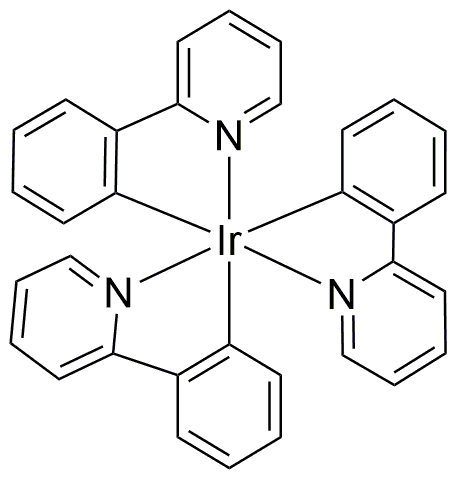
Tris(2-phenylpyridinato)iridium(III) is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs): This compound serves as an efficient phosphorescent emitter in OLEDs, enhancing light output and energy efficiency, making it ideal for display technologies.
- Chemical Sensors: Its unique luminescent properties allow for the development of sensitive chemical sensors, which can detect specific analytes in environmental monitoring and safety applications.
- Photodynamic Therapy: In the medical field, it shows promise in photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment, where its light-activated properties can selectively target and destroy cancer cells.
- Solar Cells: The compound is being explored for use in next-generation solar cells, where it can improve light absorption and conversion efficiency, contributing to renewable energy solutions.
- Catalysis: It acts as a catalyst in various organic reactions, offering advantages in reaction rates and selectivity, which is beneficial for pharmaceutical synthesis and other chemical processes.
Informations générales
Propriétés
Sécurité et réglementation
Applications
Tris(2-phenylpyridinato)iridium(III) is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs): This compound serves as an efficient phosphorescent emitter in OLEDs, enhancing light output and energy efficiency, making it ideal for display technologies.
- Chemical Sensors: Its unique luminescent properties allow for the development of sensitive chemical sensors, which can detect specific analytes in environmental monitoring and safety applications.
- Photodynamic Therapy: In the medical field, it shows promise in photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment, where its light-activated properties can selectively target and destroy cancer cells.
- Solar Cells: The compound is being explored for use in next-generation solar cells, where it can improve light absorption and conversion efficiency, contributing to renewable energy solutions.
- Catalysis: It acts as a catalyst in various organic reactions, offering advantages in reaction rates and selectivity, which is beneficial for pharmaceutical synthesis and other chemical processes.
Documents
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
Spécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Fiches de données de sécurité (FDS)
La FDS fournit des informations de sécurité complètes sur la manipulation, le stockage et l’élimination du produit.
DownloadSpécifications du produit (PS)
Le PS fournit une description complète des propriétés du produit, notamment sa composition chimique, son état physique, sa pureté et les exigences de stockage. Il détaille également les plages de qualité acceptables et les applications prévues du produit.
DownloadCertificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez des certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot et de lot se trouvent sur l'étiquette d'un produit, après les mots « Lot » ou « Lot de fabrication ».
Numéro de catalogue
Numéro de lot/série
Certificats d'origine (COO)
Ce certificat d'exploitation confirme le pays dans lequel le produit a été fabriqué, et détaille également les matériaux et composants utilisés et s'il est issu de sources naturelles, synthétiques ou autres sources spécifiques. Ce certificat peut être requis pour les douanes, le commerce et la conformité réglementaire.