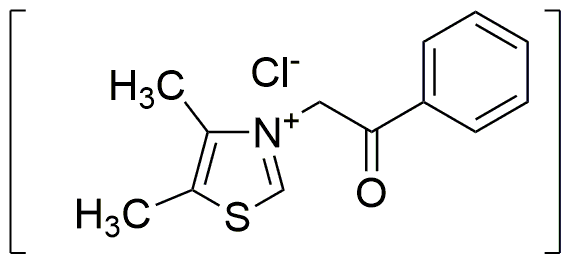
Alagebrium chloride is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Cardiovascular Health: This compound is studied for its potential to improve heart function by targeting advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which are linked to various cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes Management: Researchers are exploring its role in mitigating complications associated with diabetes, particularly by reducing the harmful effects of AGEs on tissues.
- Neuroprotection: Alagebrium chloride is being investigated for its neuroprotective properties, potentially offering benefits in conditions like Alzheimer's disease by addressing glycation-related damage in neurons.
- Pharmaceutical Development: It serves as a valuable tool in the development of new drugs aimed at treating age-related diseases, providing a basis for creating therapies that target glycation processes.
- Research on Aging: The compound is used in studies examining the biological mechanisms of aging, particularly how AGEs contribute to age-related decline and how they can be mitigated.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Alagebrium chloride is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Cardiovascular Health: This compound is studied for its potential to improve heart function by targeting advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which are linked to various cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes Management: Researchers are exploring its role in mitigating complications associated with diabetes, particularly by reducing the harmful effects of AGEs on tissues.
- Neuroprotection: Alagebrium chloride is being investigated for its neuroprotective properties, potentially offering benefits in conditions like Alzheimer's disease by addressing glycation-related damage in neurons.
- Pharmaceutical Development: It serves as a valuable tool in the development of new drugs aimed at treating age-related diseases, providing a basis for creating therapies that target glycation processes.
- Research on Aging: The compound is used in studies examining the biological mechanisms of aging, particularly how AGEs contribute to age-related decline and how they can be mitigated.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.