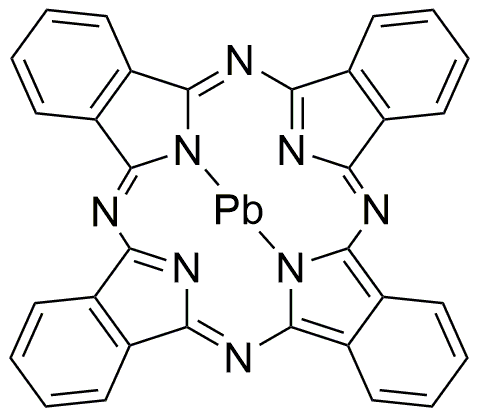
Lead(II) phthalocyanine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Colorants and Pigments: This compound is extensively used in the production of high-performance pigments for inks, coatings, and plastics, providing vibrant colors and excellent stability.
- Solar Cells: In the field of renewable energy, it serves as a key material in organic photovoltaic cells, enhancing light absorption and improving energy conversion efficiency.
- Catalysis: It acts as a catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly in the synthesis of organic compounds, offering a more efficient pathway compared to traditional methods.
- Electronics: The compound is employed in the manufacture of electronic devices, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), due to its excellent electrical conductivity and stability.
- Biomedical Applications: It shows promise in drug delivery systems and photodynamic therapy, where its ability to absorb light and generate reactive oxygen species can be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Lead(II) phthalocyanine is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Colorants and Pigments: This compound is extensively used in the production of high-performance pigments for inks, coatings, and plastics, providing vibrant colors and excellent stability.
- Solar Cells: In the field of renewable energy, it serves as a key material in organic photovoltaic cells, enhancing light absorption and improving energy conversion efficiency.
- Catalysis: It acts as a catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly in the synthesis of organic compounds, offering a more efficient pathway compared to traditional methods.
- Electronics: The compound is employed in the manufacture of electronic devices, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), due to its excellent electrical conductivity and stability.
- Biomedical Applications: It shows promise in drug delivery systems and photodynamic therapy, where its ability to absorb light and generate reactive oxygen species can be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.