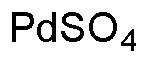Palladium(II) sulfate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Catalysis: This compound is a key catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly in organic synthesis. Its ability to facilitate reactions at lower temperatures makes it an efficient choice for researchers looking to improve reaction yields.
- Electroplating: In the electronics industry, palladium(II) sulfate is used for electroplating applications. It provides a durable and corrosion-resistant finish, essential for components in high-performance electronic devices.
- Pharmaceuticals: The compound plays a role in the synthesis of certain pharmaceutical intermediates. Its unique properties allow for the development of complex molecules, aiding in the creation of effective medications.
- Analytical Chemistry: Palladium(II) sulfate is employed in analytical techniques, such as spectrophotometry, to detect and quantify various substances. Its reliability in providing accurate results is crucial for quality control in laboratories.
- Environmental Applications: This chemical is also explored for its potential in catalytic converters, helping to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles. Its effectiveness in promoting oxidation reactions makes it a valuable asset in environmental protection efforts.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Palladium(II) sulfate is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Catalysis: This compound is a key catalyst in various chemical reactions, particularly in organic synthesis. Its ability to facilitate reactions at lower temperatures makes it an efficient choice for researchers looking to improve reaction yields.
- Electroplating: In the electronics industry, palladium(II) sulfate is used for electroplating applications. It provides a durable and corrosion-resistant finish, essential for components in high-performance electronic devices.
- Pharmaceuticals: The compound plays a role in the synthesis of certain pharmaceutical intermediates. Its unique properties allow for the development of complex molecules, aiding in the creation of effective medications.
- Analytical Chemistry: Palladium(II) sulfate is employed in analytical techniques, such as spectrophotometry, to detect and quantify various substances. Its reliability in providing accurate results is crucial for quality control in laboratories.
- Environmental Applications: This chemical is also explored for its potential in catalytic converters, helping to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles. Its effectiveness in promoting oxidation reactions makes it a valuable asset in environmental protection efforts.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.