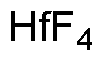Hafnium(IV) fluoride is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: This compound is essential in the production of high-k dielectrics for advanced transistors, improving the performance and efficiency of electronic devices.
- Nuclear Applications: Hafnium(IV) fluoride is used in nuclear reactors as a neutron absorber, helping to control the fission process and enhance safety.
- Optical Coatings: It serves as a material for thin-film coatings in optical devices, providing superior durability and resistance to environmental factors compared to other fluoride compounds.
- Catalysis: In chemical synthesis, this compound acts as a catalyst in various reactions, facilitating processes that require high temperatures and pressures.
- Research in Material Science: Hafnium(IV) fluoride is studied for its unique properties in developing new materials with applications in aerospace and electronics, offering potential advantages in weight reduction and thermal resistance.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Hafnium(IV) fluoride is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: This compound is essential in the production of high-k dielectrics for advanced transistors, improving the performance and efficiency of electronic devices.
- Nuclear Applications: Hafnium(IV) fluoride is used in nuclear reactors as a neutron absorber, helping to control the fission process and enhance safety.
- Optical Coatings: It serves as a material for thin-film coatings in optical devices, providing superior durability and resistance to environmental factors compared to other fluoride compounds.
- Catalysis: In chemical synthesis, this compound acts as a catalyst in various reactions, facilitating processes that require high temperatures and pressures.
- Research in Material Science: Hafnium(IV) fluoride is studied for its unique properties in developing new materials with applications in aerospace and electronics, offering potential advantages in weight reduction and thermal resistance.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.