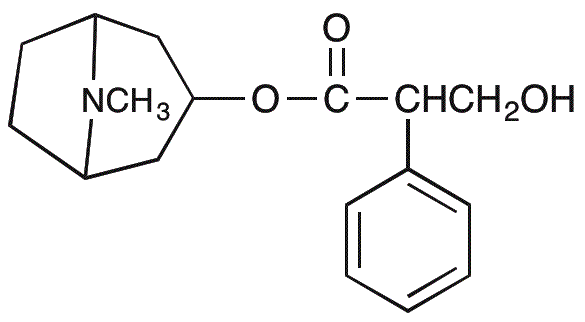
Atropine is widely utilized in research focused on various practical applications:
- Medical Treatment: Atropine is commonly used in medicine to treat bradycardia (slow heart rate) and to reduce salivation during surgeries. Its ability to block the vagus nerve helps in stabilizing heart rhythms.
- Antidote for Poisoning: It serves as an effective antidote for poisoning by organophosphates and certain types of nerve agents, providing critical care in emergency situations.
- Ophthalmology: In eye care, atropine is used to dilate pupils for diagnostic examinations and to treat certain eye conditions, enhancing patient comfort during procedures.
- Respiratory Therapy: Atropine is utilized in respiratory therapy to reduce bronchial secretions and to help manage conditions like asthma, improving breathing efficiency.
- Research Applications: In pharmacological research, it is employed to study the effects of anticholinergic drugs, aiding in the development of new therapies for various diseases.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Atropine is widely utilized in research focused on various practical applications:
- Medical Treatment: Atropine is commonly used in medicine to treat bradycardia (slow heart rate) and to reduce salivation during surgeries. Its ability to block the vagus nerve helps in stabilizing heart rhythms.
- Antidote for Poisoning: It serves as an effective antidote for poisoning by organophosphates and certain types of nerve agents, providing critical care in emergency situations.
- Ophthalmology: In eye care, atropine is used to dilate pupils for diagnostic examinations and to treat certain eye conditions, enhancing patient comfort during procedures.
- Respiratory Therapy: Atropine is utilized in respiratory therapy to reduce bronchial secretions and to help manage conditions like asthma, improving breathing efficiency.
- Research Applications: In pharmacological research, it is employed to study the effects of anticholinergic drugs, aiding in the development of new therapies for various diseases.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
*Catalog Number
*Lot Number
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.