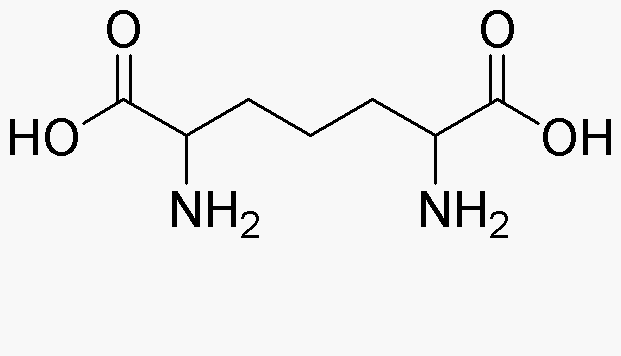
2,6-Diaminopimelic acid is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Antibiotic Development: This compound is a key building block in the synthesis of antibiotics, particularly in the production of peptidoglycan, which is essential for bacterial cell wall integrity. Its role in antibiotic formulations helps combat bacterial infections effectively.
- Biochemical Research: Researchers use it as a substrate in various enzymatic reactions, aiding in the study of metabolic pathways and enzyme kinetics. This application is crucial for understanding cellular processes and developing new biochemical assays.
- Polymer Chemistry: It serves as a monomer in the production of biodegradable polymers. These materials are increasingly important in reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainability in packaging and other applications.
- Amino Acid Synthesis: The compound is utilized in the synthesis of other amino acids, which are vital for protein production. This application is particularly relevant in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where amino acids are essential ingredients.
- Research on Genetic Engineering: It plays a role in the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) by acting as a precursor in the biosynthesis of lysine, an amino acid critical for plant and animal growth. This application supports advancements in agricultural biotechnology.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
2,6-Diaminopimelic acid is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Antibiotic Development: This compound is a key building block in the synthesis of antibiotics, particularly in the production of peptidoglycan, which is essential for bacterial cell wall integrity. Its role in antibiotic formulations helps combat bacterial infections effectively.
- Biochemical Research: Researchers use it as a substrate in various enzymatic reactions, aiding in the study of metabolic pathways and enzyme kinetics. This application is crucial for understanding cellular processes and developing new biochemical assays.
- Polymer Chemistry: It serves as a monomer in the production of biodegradable polymers. These materials are increasingly important in reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainability in packaging and other applications.
- Amino Acid Synthesis: The compound is utilized in the synthesis of other amino acids, which are vital for protein production. This application is particularly relevant in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where amino acids are essential ingredients.
- Research on Genetic Engineering: It plays a role in the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) by acting as a precursor in the biosynthesis of lysine, an amino acid critical for plant and animal growth. This application supports advancements in agricultural biotechnology.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.