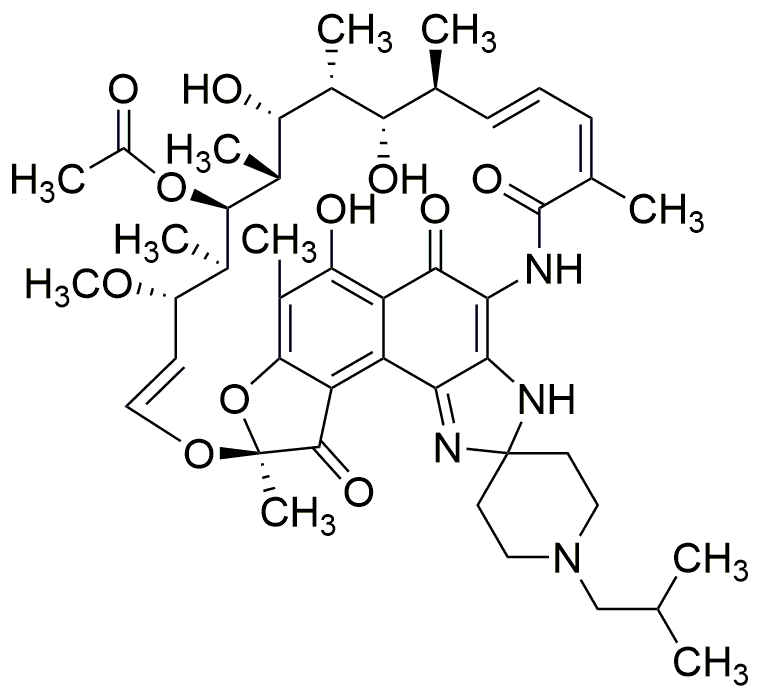
Rifabutin is widely utilized in research focused on
- Treatment of Tuberculosis: Primarily used as an antibiotic to treat tuberculosis, especially in patients with HIV, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing the risk of drug resistance.
- HIV Co-infection Management: Effective in managing opportunistic infections in HIV-positive patients, providing a critical option for healthcare providers in improving overall patient health.
- Pharmaceutical Research: Employed in the development of new formulations and delivery methods, aiding researchers in creating more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
- Clinical Trials: Frequently used in clinical studies to evaluate its efficacy and safety, contributing to the advancement of medical knowledge and treatment protocols.
- Public Health Initiatives: Plays a role in global health programs aimed at controlling tuberculosis, particularly in high-burden countries, supporting efforts to reduce disease prevalence.
Información general
Propiedades
Seguridad y normativas
Aplicaciones
Rifabutin is widely utilized in research focused on
- Treatment of Tuberculosis: Primarily used as an antibiotic to treat tuberculosis, especially in patients with HIV, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing the risk of drug resistance.
- HIV Co-infection Management: Effective in managing opportunistic infections in HIV-positive patients, providing a critical option for healthcare providers in improving overall patient health.
- Pharmaceutical Research: Employed in the development of new formulations and delivery methods, aiding researchers in creating more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
- Clinical Trials: Frequently used in clinical studies to evaluate its efficacy and safety, contributing to the advancement of medical knowledge and treatment protocols.
- Public Health Initiatives: Plays a role in global health programs aimed at controlling tuberculosis, particularly in high-burden countries, supporting efforts to reduce disease prevalence.
Documentos
Hojas de datos de seguridad (HDS)
La SDS proporciona información de seguridad completa sobre la manipulación, el almacenamiento y la eliminación del producto.
Especificación del producto (PS)
La PS proporciona un desglose completo de las propiedades del producto, incluida la composición química, el estado físico, la pureza y los requisitos de almacenamiento. También detalla los rangos de calidad aceptables y las aplicaciones previstas del producto.
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque certificados de análisis (COA) ingresando el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote y de partida se pueden encontrar en la etiqueta de un producto después de las palabras "Lote" o "Lote".
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificados de origen (COO)
Este certificado de origen confirma el país en el que se fabricó el producto y también detalla los materiales y componentes utilizados en él y si se deriva de fuentes naturales, sintéticas u otras fuentes específicas. Este certificado puede ser necesario para cumplir con las normativas aduaneras, comerciales y regulatorias.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Hojas de datos de seguridad (HDS)
La SDS proporciona información de seguridad completa sobre la manipulación, el almacenamiento y la eliminación del producto.
DownloadEspecificación del producto (PS)
La PS proporciona un desglose completo de las propiedades del producto, incluida la composición química, el estado físico, la pureza y los requisitos de almacenamiento. También detalla los rangos de calidad aceptables y las aplicaciones previstas del producto.
DownloadCertificados de análisis (COA)
Busque certificados de análisis (COA) ingresando el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote y de partida se pueden encontrar en la etiqueta de un producto después de las palabras "Lote" o "Lote".
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificados de origen (COO)
Este certificado de origen confirma el país en el que se fabricó el producto y también detalla los materiales y componentes utilizados en él y si se deriva de fuentes naturales, sintéticas u otras fuentes específicas. Este certificado puede ser necesario para cumplir con las normativas aduaneras, comerciales y regulatorias.