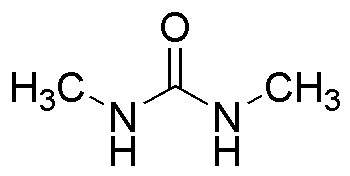
1,3-Dimethylurea is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Agriculture: It serves as a nitrogen source in fertilizers, promoting plant growth and enhancing crop yields.
- Pharmaceuticals: This compound is used in the synthesis of various medicinal agents, contributing to the development of new drugs.
- Polymer Science: It acts as a building block in the production of polymers, improving material properties such as strength and durability.
- Biochemistry: Researchers utilize it in studies related to enzyme activity and protein interactions, aiding in the understanding of biological processes.
- Environmental Science: It is employed in the formulation of biodegradable materials, addressing sustainability challenges in various industries.
Información general
Propiedades
Seguridad y normativas
Aplicaciones
1,3-Dimethylurea is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Agriculture: It serves as a nitrogen source in fertilizers, promoting plant growth and enhancing crop yields.
- Pharmaceuticals: This compound is used in the synthesis of various medicinal agents, contributing to the development of new drugs.
- Polymer Science: It acts as a building block in the production of polymers, improving material properties such as strength and durability.
- Biochemistry: Researchers utilize it in studies related to enzyme activity and protein interactions, aiding in the understanding of biological processes.
- Environmental Science: It is employed in the formulation of biodegradable materials, addressing sustainability challenges in various industries.
Documentos
Hojas de datos de seguridad (HDS)
La SDS proporciona información de seguridad completa sobre la manipulación, el almacenamiento y la eliminación del producto.
Especificación del producto (PS)
La PS proporciona un desglose completo de las propiedades del producto, incluida la composición química, el estado físico, la pureza y los requisitos de almacenamiento. También detalla los rangos de calidad aceptables y las aplicaciones previstas del producto.
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque certificados de análisis (COA) ingresando el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote y de partida se pueden encontrar en la etiqueta de un producto después de las palabras "Lote" o "Lote".
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificados de origen (COO)
Este certificado de origen confirma el país en el que se fabricó el producto y también detalla los materiales y componentes utilizados en él y si se deriva de fuentes naturales, sintéticas u otras fuentes específicas. Este certificado puede ser necesario para cumplir con las normativas aduaneras, comerciales y regulatorias.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Hojas de datos de seguridad (HDS)
La SDS proporciona información de seguridad completa sobre la manipulación, el almacenamiento y la eliminación del producto.
DownloadEspecificación del producto (PS)
La PS proporciona un desglose completo de las propiedades del producto, incluida la composición química, el estado físico, la pureza y los requisitos de almacenamiento. También detalla los rangos de calidad aceptables y las aplicaciones previstas del producto.
DownloadCertificados de análisis (COA)
Busque certificados de análisis (COA) ingresando el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote y de partida se pueden encontrar en la etiqueta de un producto después de las palabras "Lote" o "Lote".
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificados de origen (COO)
Este certificado de origen confirma el país en el que se fabricó el producto y también detalla los materiales y componentes utilizados en él y si se deriva de fuentes naturales, sintéticas u otras fuentes específicas. Este certificado puede ser necesario para cumplir con las normativas aduaneras, comerciales y regulatorias.