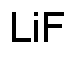Lithium fluoride is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Optical Applications: Its unique optical properties make it an excellent choice for manufacturing lenses and windows in ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy, enhancing the performance of optical devices.
- Nuclear Fusion Research: The compound is used in fusion reactors as a coolant and a material for breeding tritium, playing a critical role in advancing clean energy technologies.
- Dental Materials: In dentistry, lithium fluoride is incorporated into dental cements and restorative materials, providing improved durability and biocompatibility for dental applications.
- Electrolytes in Batteries: It serves as a solid electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries, contributing to higher efficiency and longer life cycles compared to traditional liquid electrolytes.
- Radiation Detection: The compound is utilized in radiation detection devices, where its ability to emit light when exposed to radiation makes it valuable for safety and monitoring applications.
General Information
Properties
Safety and Regulations
Applications
Lithium fluoride is widely utilized in research focused on:
- Optical Applications: Its unique optical properties make it an excellent choice for manufacturing lenses and windows in ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy, enhancing the performance of optical devices.
- Nuclear Fusion Research: The compound is used in fusion reactors as a coolant and a material for breeding tritium, playing a critical role in advancing clean energy technologies.
- Dental Materials: In dentistry, lithium fluoride is incorporated into dental cements and restorative materials, providing improved durability and biocompatibility for dental applications.
- Electrolytes in Batteries: It serves as a solid electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries, contributing to higher efficiency and longer life cycles compared to traditional liquid electrolytes.
- Radiation Detection: The compound is utilized in radiation detection devices, where its ability to emit light when exposed to radiation makes it valuable for safety and monitoring applications.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
Product Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
The SDS provides comprehensive safety information on handling, storage, and disposal of the product.
DownloadProduct Specification (PS)
The PS provides a comprehensive breakdown of the product’s properties, including chemical composition, physical state, purity, and storage requirements. It also details acceptable quality ranges and the product's intended applications.
DownloadCertificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Número de catálogo
Número de lote/lote
Certificates Of Origin (COO)
This COO confirms the country where the product was manufactured, and also details the materials and components used in it and whether it is derived from natural, synthetic, or other specific sources. This certificate may be required for customs, trade, and regulatory compliance.